Research
Research and Publications
Signal Analysis Techniques for Resting State Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
April 2017 - December 2022
Functional Near-InfraRed Spectroscopy (fNIRS) has widespread acceptance as a non-invasive neuroimaging modality of monitoring cerebral perfusion and brain functional activities. It offers advantages such as safety, affordability and portability. FNIRS uses light in near infra-red spectrum (600-900nm) to penetrate human brain tissue and estimates the oxygenation condition based on the proportion of light absorbed. The focus for the research is signal processing methods used in fNIRS.
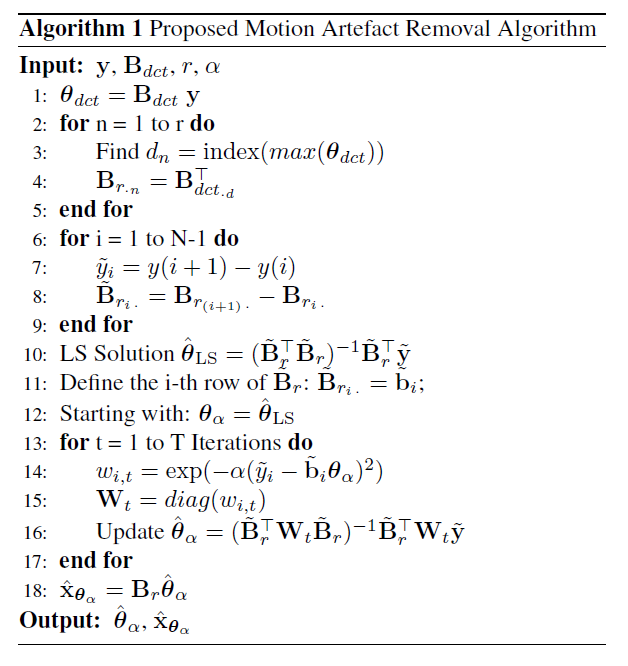
Motion Artefact Removal
Artefacts and noise need to be separated from fNIRS physiological signals. This project focuses on removing motion-related artefacts. A new motion artefact removal algorithm based on robust parameter estimation is proposed. Results illustrate that the proposed algorithm can outperform the state-of-art algorithms in removing motion artefacts. Moreover, the proposed algorithm is robust in estimating the parameters under different interference conditions.
Violation of the Whiteness Assumption in fNIRS RSFC
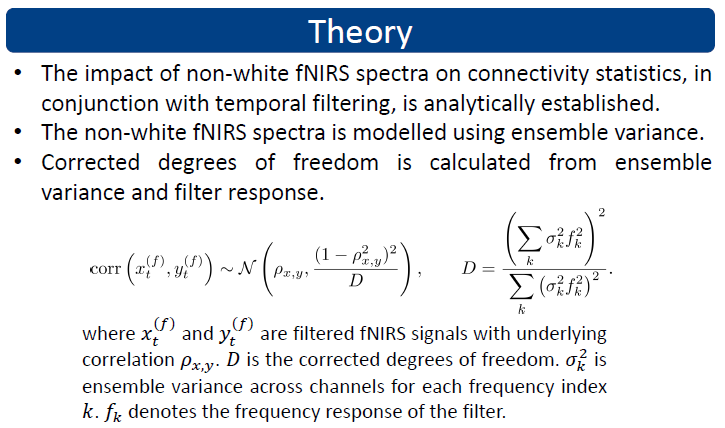
Resting-state functional connectivity (FC) methods applied to fNIRS data assume that the signals are white. If this assumption is violated, statistical tests are invalid and connectivity may be artificially recorded. Temporal filtering is known tocause a violation of the whiteness assumption, and corrections to statistical tests of connectivity have been proposed for fMRI data. However, such corrections assume that unfiltered signals are white. It is known that fNIRS signals are typically not white prior to preprocessing. We propose a correction to statistical tests of functional connectivity, that accounts for both non-white fNIRS data and the further effects of filtering.
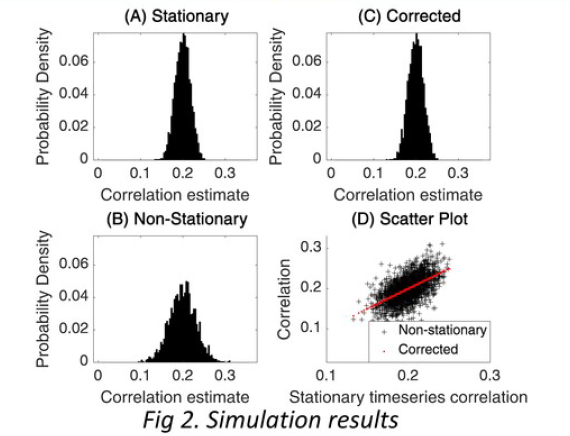
Violation of the Stationarity Assumption in fNIRS RSFC
Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS) signals are contaminated by various sources of noise, including physiological noise and motion artefacts, both of which can change over time. We empirically establish the non-stationarity of fNIRS signals, identifying the distribution of the time-varying signal power. Non-stationarity of fNIRS signals violates the stationarity assumption imposed by resting-state functional connectivity (RSFC) measures, invalidating statistical significance tests. We propose a simple correction for the time-varying signal power of fNIRS signals that restores the integrity of RSFC analyses. The correction is drawn from a similar method proposed for non-stationary functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) data, that was analytically established to restore the voracity of RSFC tests.
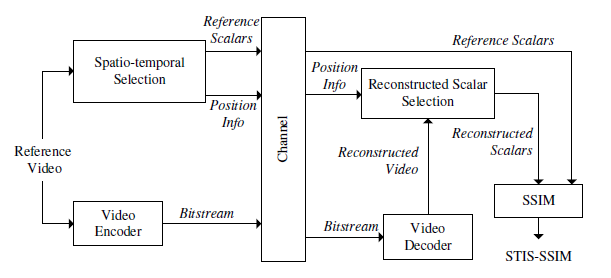
A Very Low Complexity Reduced Reference Video Quality Metric
June 2014 - December 2014
This paper presents a reduced reference video quality metric that exploits contrast and motion sensitivity characteristics of the HVS to perform a spatio-temporal selection of reference data. Spatio-temporal selection is realised through mapping of wavelet subbands to contrast sensitivity and through motion analysis. The proposed method is integrated with a modified SSIM-based framework to produce STIS-SSIM, a very low complexity reduced reference metric. The metric is shown to offer significant performance improvement over many existing full reference and reduced reference video quality metrics when tested on the LIVE video database.